Tokenization has become a synonym for ease, trust and security, since it is one of the best data protection strategies that can be integrated into different payment ecosystems. The benefits it brings to both sellers and consumers have made it possible for tokenization to spread so quickly.
What is tokenization?
Tokenization is the protection of the sensitive data or PAN (principal account number) of a card by means of replacing it with an algorithmically generated number called token. It is mainly used to prevent credit card fraud.
This functionality allows a website to store all the payment information of a user without having to keep sensitive information on the site, so you can make periodic collections or facilitate payment in 1 click in your online store.
Once the token is created, tokenization is irreversible, there is no mathematical relationship between the original number and the token, only the system that generated the token in the first place is capable of performing the reverse process, so if there was a gap in the web the leaked data would be absolutely useless to the thief.
How does tokenization work?
The tokens are created by companies such as VISA and Mastercard, among others, which act as Token Service Providers (TSP) and send them to mobile payment or e-commerce platforms so that they can use them in transactions instead of using the customer’s actual card data.
This way, when a user enters their card details in a virtual wallet such as Google Pay or Apple Pay, these platforms request the ‘token’ from one of these providers, who must first ask the customer’s bank for verification of the data.
Once the data is verified, they generate the token and send it to the user’s device. After this unique number is created, it is irreversibly and irreplaceably linked to the customer’s device.
So every time the user makes a payment, the platform can authorize the operation just by sharing this code, without having to expose the real data.
In addition, since tokenization is a fully PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliant solution, many platforms are opting to facilitate the adoption of this new secure payment system for their customers.
Tokenization on the payment gateway
To better understand the process of converting the original payment data to a token, let’s take a look at what happens from the time a customer uses their credit card to the time the payment is processed.
- A credit card is swiped at an ATM or used for an online transaction.
- The credit card number is passed to the tokenization system.
- The tokenization system generates a random 16-character sequence to replace the original credit card number.
- The tokenization system returns the newly generated 16 random characters to the POS machine or e-commerce site to replace the customer’s credit card number in the system.
Tokenization process with Truust
At Truust, the tokenization process works as follows.
The Truust API receives the request to save the card from the user, Truust communicates with the tokenization service of the acquiring bank (RedSys, Addon Payments, etc).
A token is then generated, which can be used by the merchant to charge subsequent purchases, as shown in the diagram below.
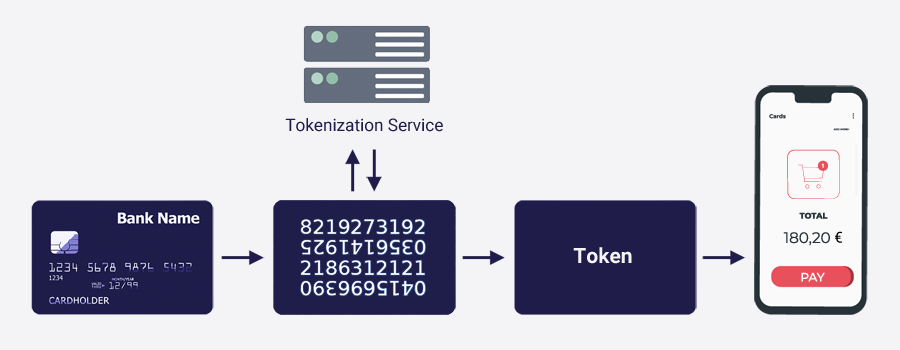
This way, your business never stores, processes or transfers the PAN: only the token.
The advantage of an off-platform tokenization service is that it prevents computer attacks from obtaining any kind of sensitive information, neither financial nor personal.
Advantages of tokenization
The major advantages of implementing a tokenization service in your platform are the following:
- At all times the financial institution keeps the control of customer data, and external systems never have access to them.
- Since the tokens are not mathematically linked to the original value, security is maximized.
- It facilitates payment on subsequent visits by avoiding the need to re-enter data each time the user wants to make a new purchase.
Tokenization in payment processing: use cases
The fact is that tokenization is extraordinarily useful for various types of online transactions. We can distinguish three payment scenarios in which tokenization is playing an increasingly important role.
- The first case is for businesses that need to securely store their users’ credit card information so that they can charge a subscription or generate a recurring payment.
- The second is for online stores or marketplaces where merchants want to offer their users one-click checkouts.
- And the third is for the so-called mobile proximity payments (NFC / Near Field Communications), such as Apple Pay and Android Pay.
Below, we explain how tokenization helps you protect yourself in these payment scenarios.
#1 Tokenization in the payment of subscriptions
Imagine a streaming-music service needs to process customers’ subscription payments on a monthly and recurring basis. Imagine if this service had to email, call or send an SMS to its users every month to get payment details.
This would result in a significant process overload for the service, as a lot of effort would be required to manage the payment updates. The users’ experience would also be affected, which could result in more customers deciding not to pay that month or, even worse, losing interest in the service.
However, thanks to tokenization, this arduous process will be unnecessary: the company can recharge its customers monthly without the need to display the original card information.
Truust offers several solutions as a payment partner to businesses at any size. For more information, get in touch with our team .
#2 Tokenization in e-commerce
Tokenization also helps to protect payments on online purchases.
Let’s take an example of a website that sells mobile phone cases.
The customer, after making a purchase has the option to save the data from their card for future purchases, having an integrated system of tokenization, the data are converted into tokens and thus fully secured.
Even in the hypothetical case that the web is hacked. The only thing the hacker could see would be the tokens, i.e. useless information that cannot be deciphered.
Let’s take the tokenization of Apple Pay as an example.
#3 Tokenization in mobile wallets: Apple Pay and Android Pay
After taking a photo of your credit card and saving it to your iPhone from the app called “Wallet”, Apple sends the data to the bank or network that issued the card, which replaces your card data with a series of randomly generated numbers (the token). This random number is sent back to Apple, which programs it into the phone.
This means that no information useful to scammers can be extracted from the number stored in the mobile phone.
Tokenization vs Encryption
Although tokenization and encryption have certain similarities, when it comes to cloud data protection, these security technologies differ from each other. The major difference is the security method each system uses.
To put it simply, whereas tokenization technology protects data by means of using a token, encryption uses a key.
This means that tokenization transforms sensitive data into an irreversible number without sensitive information (token), and securely stores that original sensitive information outside its original environment.
In contrast, encryption encodes the content of a data element where it resides with a key shared between the person who is encrypting the data and the person who needs to decrypt it.
To access the original data, tokenization exchanges the token for the sensitive data, while encryption decodes the encrypted data to reveal its sensitive form.
Both solutions have great advantages when it comes to securely storing customer data:
- Encryption is ideal for unstructured fields or databases of information that are not frequently exchanged or stored in multiple systems.
- Tokenization is ideal for structured data, such as Social Security and credit card numbers, which must be kept on file to verify identities and be easily accessible for future use, such as financial transactions and online purchases.
| Criteria | TOKENIZATION | ENCRYPTION |
| The PAN (principal account number) is displayed | X | |
| Mathematically reversible | X | |
| Reduces the scope of the PCI | X | |
| Payment flexibility: refunds, chargebacks, recurring payments, etc. | X | |
| Key rotation required | X | |
| End-to-End Security | X | |
| Low cost per transaction | X | |
| The format is consistent with traditional credit card fields | X | |
| It is centrally managed | X | |
| Established security | X |
In short, tokenization is a complex concept, but it is useful to understand how it works in order to see how useful it can be in the payment processing industry, where it is becoming increasingly important. It is an exciting revolution that makes payment processing more secure.
REFERENCES
https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/tokenization
https://medium.com/coreledger/what-is-tokenization-everything-you-should-know-1b2403a50f0e
https://www.adyen.com/knowledge-hub/guides/tokenization-payment-technology-guide#how
https://blockgeeks.com/guides/security-tokens/
