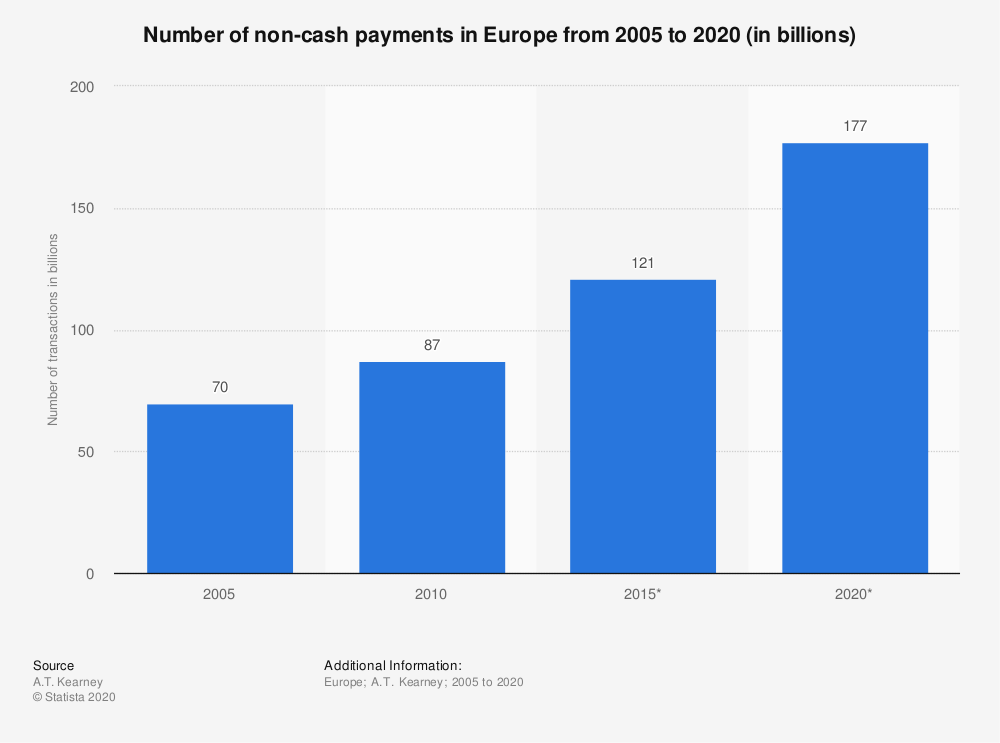
Cashless payment is becoming more and more important – not only for online shopping but also for everyday purchases. We already wrote an article about Cashless Stadiums: An Essential Solution For The Future that explains the new cashless entertainment experience.
Consumers have the choice between different methods. Depending on the provider, cards, smartphone apps or online services can be used.
What is a cashless payment?
Together with cash payments and so-called semi-cash payments, cashless payments make up the entire payment traffic. As the name suggests, cashless payment transactions are all payments where no cash is moved at all.
Especially in today’s society, cashless payments represent a standard that cannot be imagined without. There are now almost countless ways to pay without cash.
For cashless payments to be possible at all, the basic condition is that the parties involved – whether private individuals, companies or government institutions – have a bank account.
Cashless vending machines
Against the backdrop of the rise of cashless payments, it is unsurprising that the vending industry has an important role to play in this area.
From a customer perspective, it is inconvenient when vending machines only allow cash payments, and from a vendor perspective, using cash can be complex and costly.
Now the vending industry is embracing smart technology, which has radically changed the public perception of a typical vending machine.
The adoption of cashless vending machines began some time ago with the integration of chip-and-pin devices, but there is still much innovation potential.
How is cashless payment done?
Usually, credit and financial institutions are involved in cashless payments, which carry out the cashless payment or book money payment accordingly. By transferring the necessary data, the transfer of a sum of money then takes place from bank account to bank account.
In online banking, for example, the data for a transfer is encrypted and transmitted to the bank via the Internet. The data usually contains instructions that specify how much money is to be transferred, from which account and at what time.
When payments are made at card terminals, the data is transferred via a TCP/IP connection. If, for example, payment is made by card in a shop and the payment is confirmed by PIN, the financial institution transfers the amount from the shopper’s account to the respective card institution – e.g. Mastercard.
After verification and authorisation, the card institute forwards the money to the merchant accordingly.
Cashless payment systems
Cashless payment systems offer buyers a simple, efficient and secure way to pay for their online purchases.
Cashless payment systems have replaced the physical currency in various ways to improve the transfer of cash from one account to another. Each system has unique features, mechanisms and qualities that work with different types of devices.
Most online payment systems are becoming increasingly popular because of their convenience.
As a technological evolution, cashless payment systems have led to the emergence of cashless payment applications.
Another example of this evolution is the digital wallet, a system that allows transactions to be made through a computer or smartphone. This type is linked to the user’s bank account to make actual payments.
With a cashless system, you can check your balance, budget and then pay your bill without leaving your mobile device.
The best thing about a cashless payment system is that it is simple, efficient and secure.
Advantages of cashless transactions
Cashless transactions bring both advantages and disadvantages compared to paying with notes and coins.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Which country is completely cashless?
Sweden is paving the way to becoming the world’s first cashless society in March 2023.
In 2023, Sweden will proudly become the world’s first cashless country with a 100% digital economy. Around 80% of Swedes currently use cards, with 58% of payments made by card and only 6% by cash, according to the Swedish Central Bank.
Electronic payments are growing rapidly, with more and more restaurants and shops no longer accepting cash payments. Mobile payment services are also facilitating people-to-people payments.
The entire Swedish population is covered by mobile phones.
In the past few years, almost all purchases in Sweden have been paid for electronically: debit/credit cards with a chip and pin instead of the old-fashioned magnetic strip, contactless technology, mobile card payments such as iZettle, or the Swish mobile app, developed specifically to help Swedes live cashlessly.
For a start, coins and banknotes won’t disappear completely. But no one will be able to use them in a practical sense. They will become pure collector’s items and be included in museum collections.
The way the Nordic countries are moving quickly to a cashless lifestyle contrasts with the southern European countries, where cash is still a strong means of payment.
Moreover, in some Southern European cities, some establishments only accept cash. This is in stark contrast to Northern Europe, where cash is no longer accepted in most places.
Conclusion
Cash contributes to better control over spending and guarantees us privacy.
All our inputs and outputs are documented and we are deprived of the possibility to pay anonymously. We give up our security in favour of convenience.
The wallet would therefore no longer be filled with heavy small change, but with personal data.
